How to recognize images created by a neural network
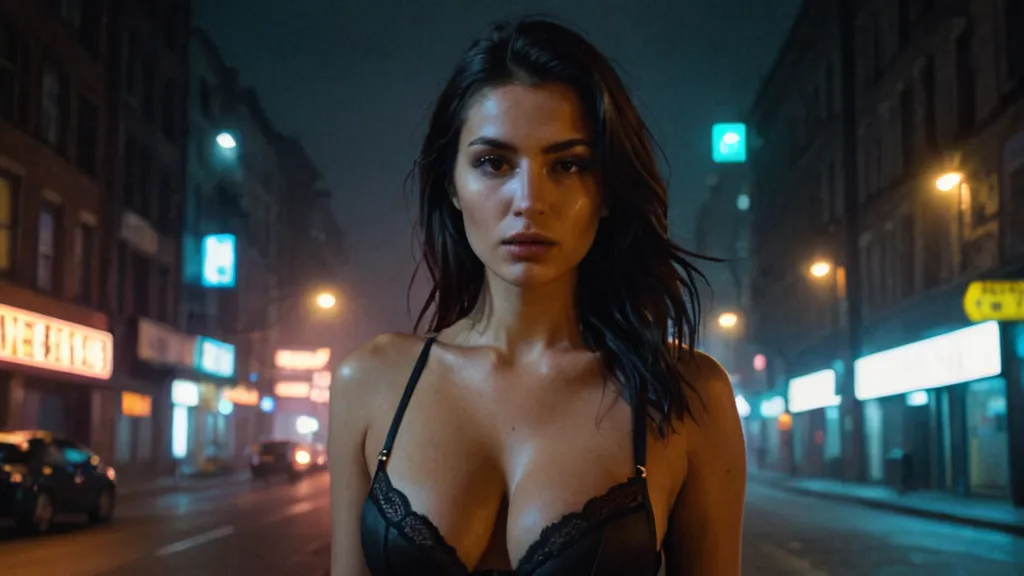

Sometimes the best AI image detector is your own eyes. Let’s start with the bad news: it’s become really hard to identify AI-generated images. Signs that used to be obvious – distorted hands and jumbled text – are now rarer and rarer as AI models rapidly improve. Nowadays, it is no longer easy to distinguish between images created with popular tools such as Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, DALL-E and Gemini. Moreover, AI images are increasingly misleading people, which poses a serious problem for the spread of misinformation. The good news is that recognizing AI-generated images is still possible, although it requires more effort than before.
It is still possible to recognize AI-generated images.
AI image detectors – beware
.
These tools use computer vision to analyze pixel patterns and determine the likelihood that an image was created by AI. This means that AI detectors are not completely reliable, but can help the average person understand whether an image is worth paying closer attention to, especially if it doesn’t seem suspicious at first glance.
An AI image detector can help the average person understand whether an image is worth paying closer attention to, especially if it doesn’t seem suspicious at first glance.
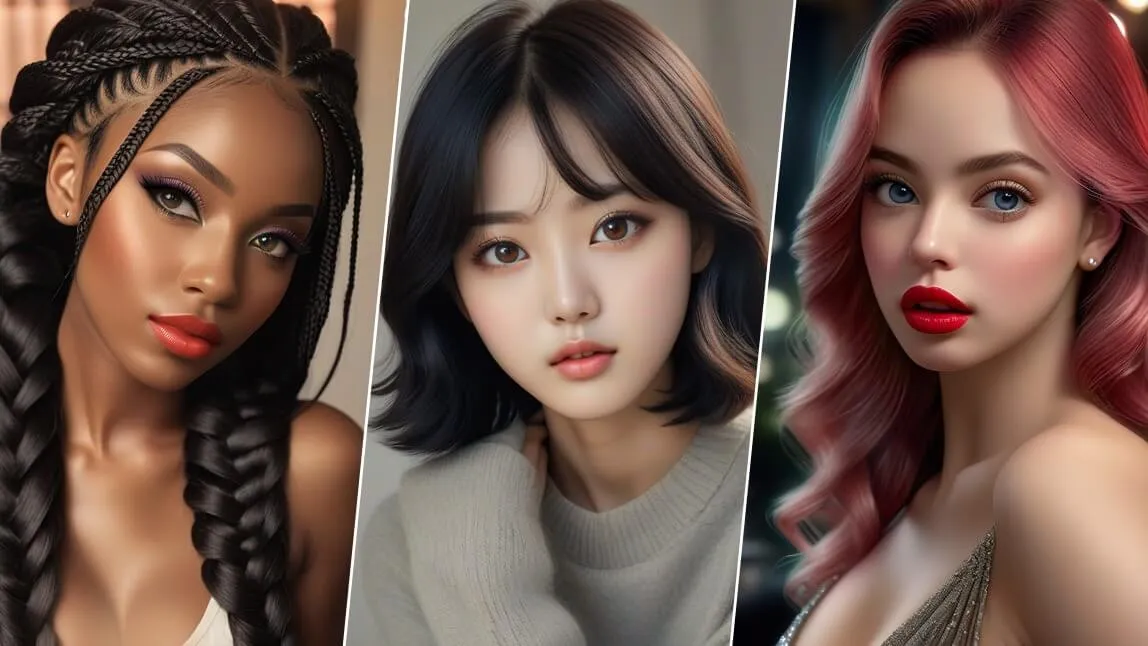

“Unfortunately, for the human eye – and there are studies about this – the chance of detecting the authenticity of an image is about 50/50,” says Anatoly Kvitnitsky, CEO of AI or Not, a platform designed to detect images created by AI. “But for AI detectors, thanks to pixel patterns, the probability of detection remains high, even despite improvements in the models.” Kvitnicki claims that AI or Not achieves 98 percent accuracy on average. Other AI detectors that show high success rates include Hive Moderation, SDXL Detector on the Hugging Face platform, and Illuminarty. We tested ten AI-generated images on all of these detectors to evaluate their performance.
.
AI or Not
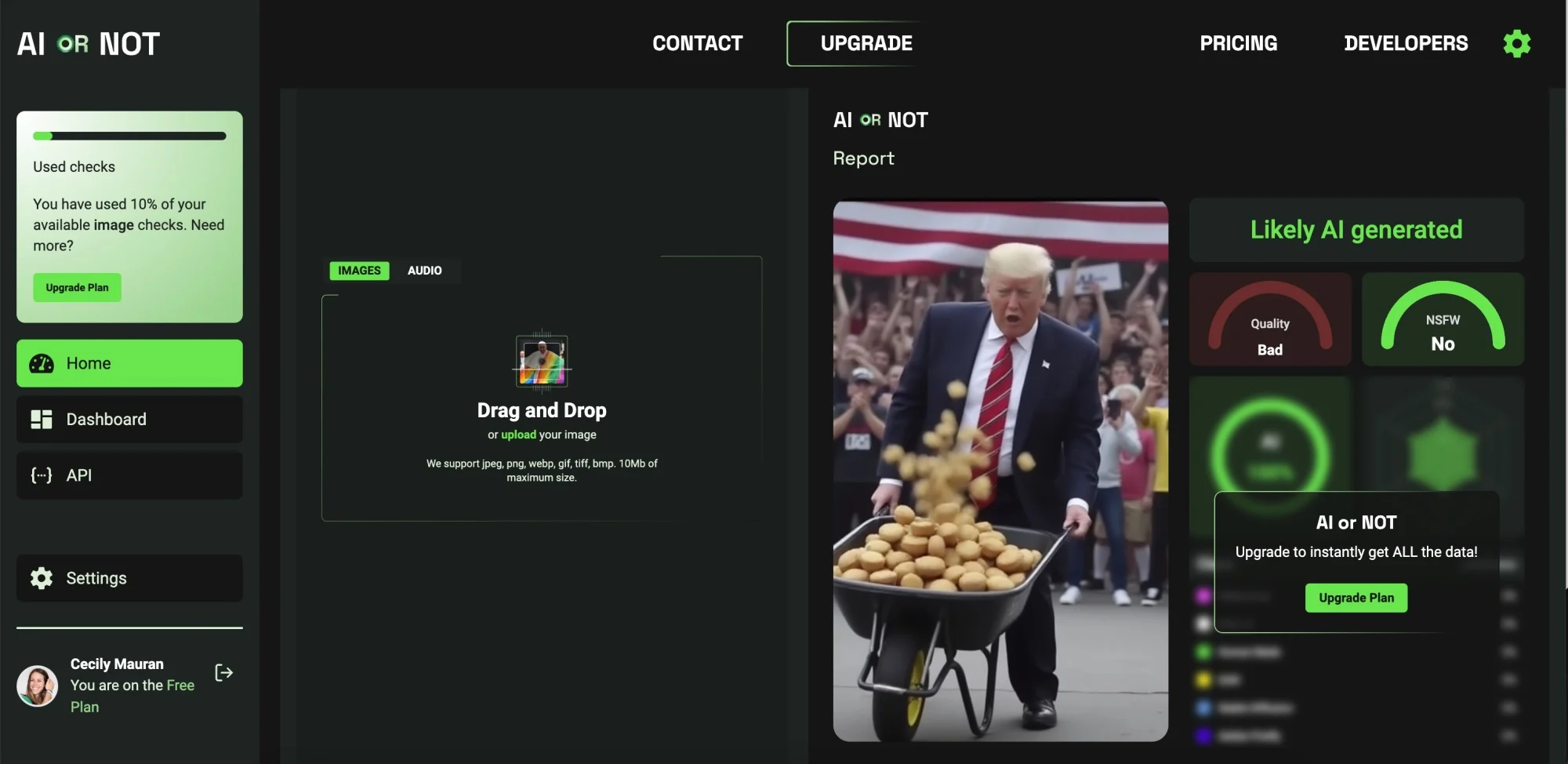
AI or Not gives a simple answer «yes» or «no» unlike other AI image detectors, but correctly determined that the image was created by an AI. With the free plan, you can upload up to 10 images per month. We tried 10 images and had an 80 percent success rate.
We tried 10 images and got an 80 percent success rate.
Hive Moderation
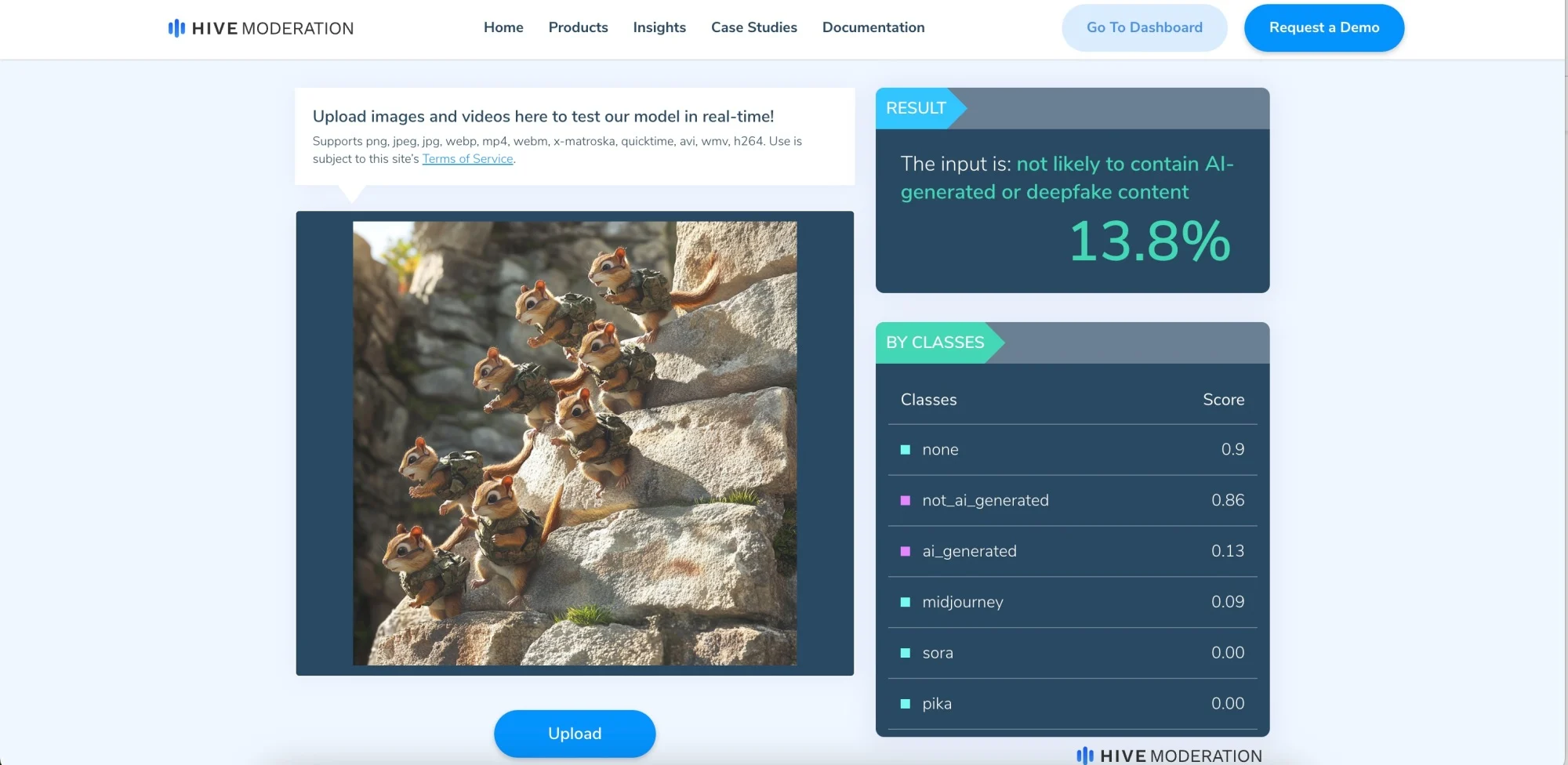
We tested the free demo tool Hive Moderation on more than 10 different images and got a 90 percent overall success rate, which meant there was a high probability that the images were created by AI. However, the tool failed to recognize the AI characteristics of an artificial image of an army of chipmunks climbing a cliff.
SDXL Detector
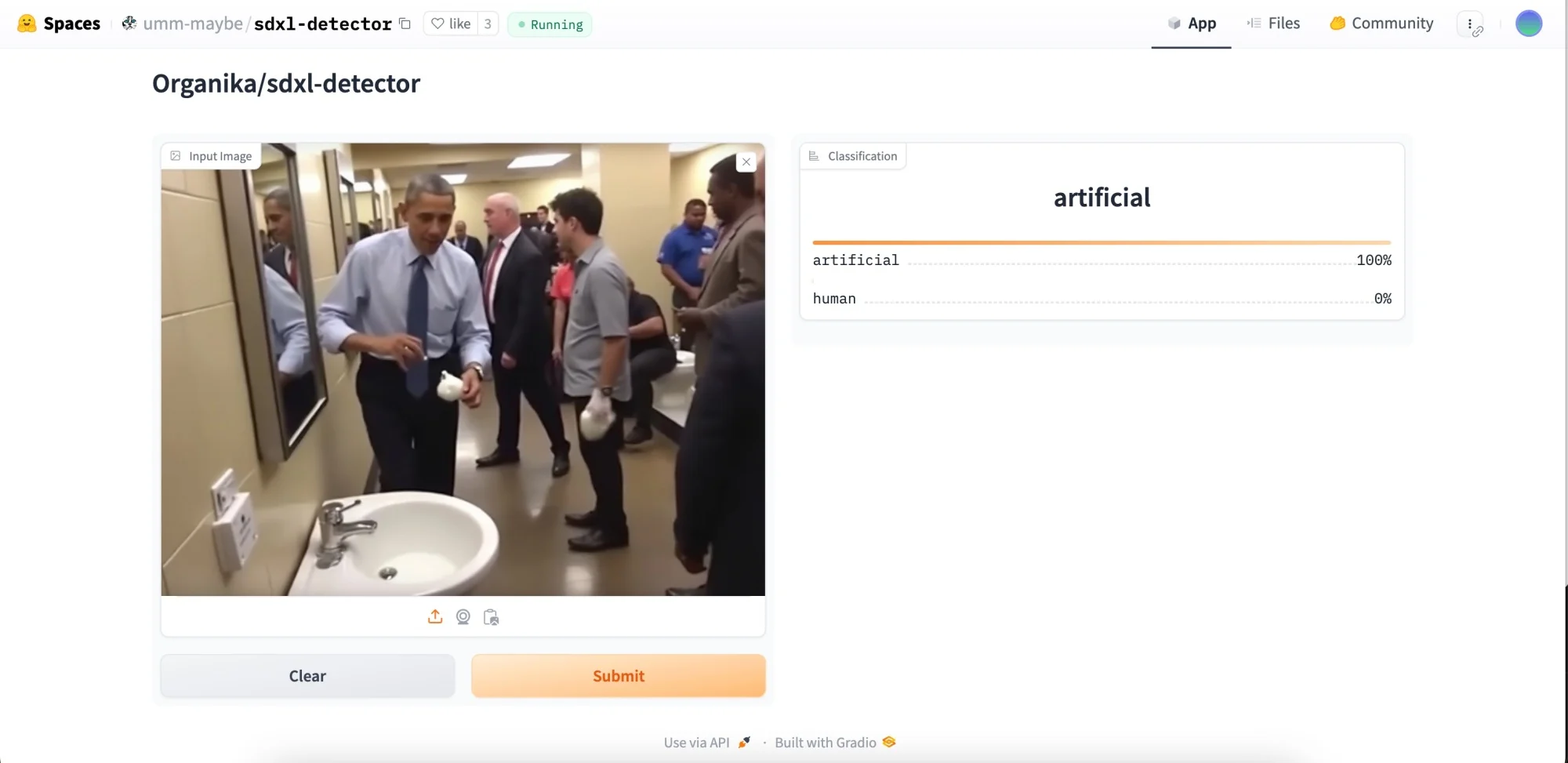
SDXL Detector on Hugging Face takes a few seconds to load and you may get an error on the first try, but it is completely free. This tool also provides percent probability. It showed that 70 percent of the AI images had a high probability of being generated by AI.
Illuminarty
.
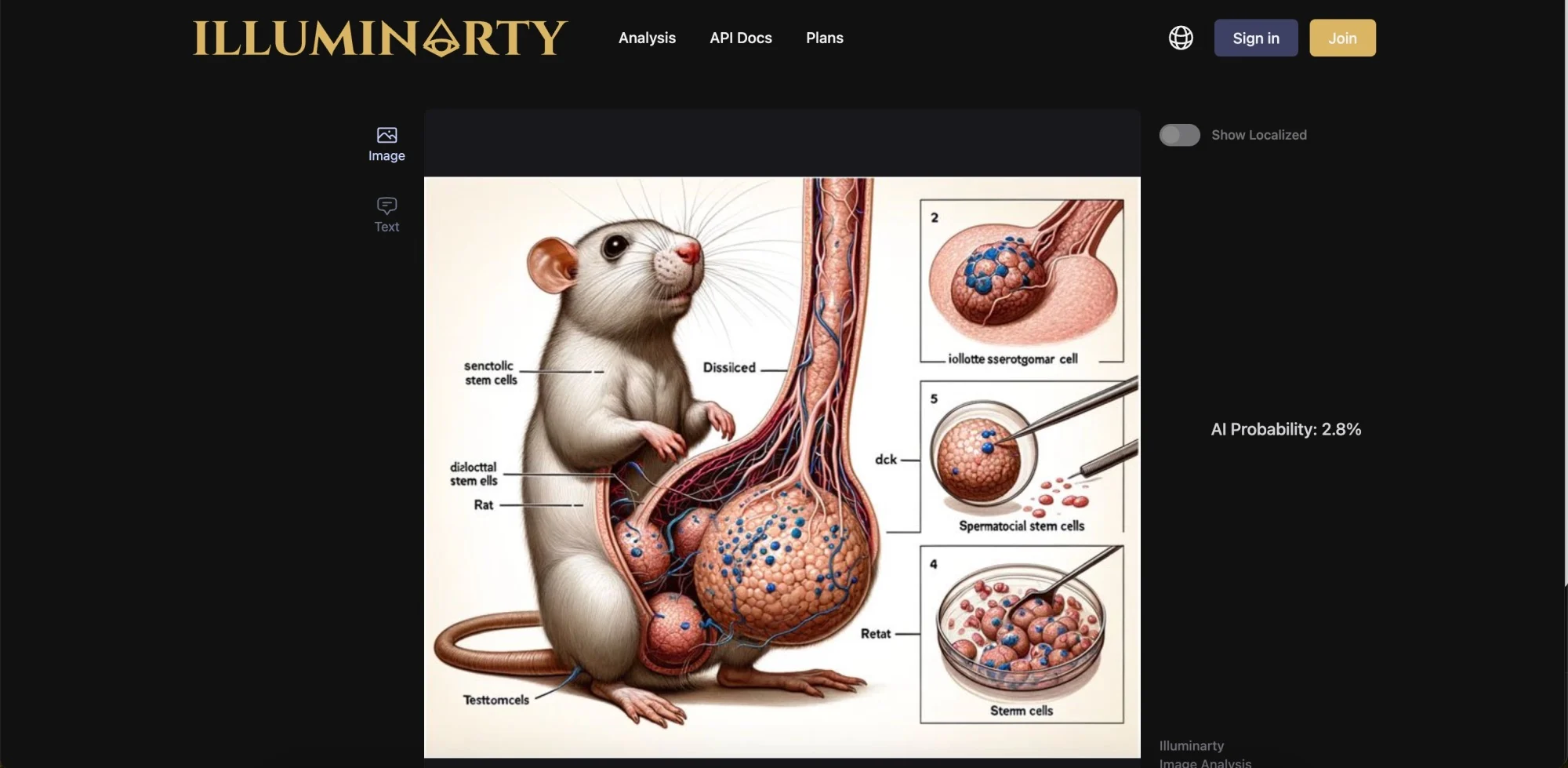
Illuminarty has a free plan that provides basic AI image detection. Of the 10 AI images we uploaded, only 50 percent were classified as having a very low probability of being created by AI. To the dismay of rodent biologists, it gave the infamous rat dick image a low probability of being created by an AI.
And to the dismay of rodent biologists, it gave the infamous rat dick image a low probability of being created by an AI.
As you can see, AI detectors are reasonably accurate in most cases, but not infallible, and should not be used as the only way to authenticate an image. Sometimes they can detect deceptive AI images even if they look realistic, and sometimes they get it wrong with images that were clearly created by the AI. That’s why it’s best to use a combination of methods.
Other tips and tricks
Good old reverse image search
Another way to detect AI images is a simple reverse image search, which is what Bamshad Mobasher, professor of computer science and director of the Center for Web Intelligence in the College of Computing and Digital Media at DePaul University in Chicago, recommends. By uploading an image to Google Images or another reverse image search tool, you can trace the image’s origin. If a photo depicts a seemingly real event, “you can determine that it’s a fake or that the event didn’t actually happen,” Mobasher said.
Mobasher said.
Google Tool «About Image»
Google Search also has an “About Image” feature that provides contextual information, such as when an image was first indexed and where else it has appeared on the web. You can find it by clicking on the three-dot icon in the upper right corner of the image.
It all comes down to AI literacy
None of the above methods are useful unless you first consider whether what you’re seeing is AI-created. Just as media literacy became a popular concept as misinformation spread during the 2016 election, AI literacy is the first line of defense for determining authenticity. AI researchers Durie Long and Brian Magerko define AI literacy as “a set of competencies that enable people to critically evaluate AI technologies; interact and collaborate effectively with AI; and use AI as a tool online, at home, and in the workplace.”
An AI literacy is a set of competencies that enables people to critically evaluate AI technologies; interact and collaborate effectively with AI; and use AI as a tool online, at home, and in the workplace.
Knowing how generative AI works and what to look out for is key. “It may sound trivial, but taking the time to check the source and provenance of the content you see on social media is a good place to start,” Luccioni says.
“It’s a good place to start,” says Luccioni.
Start by asking who published the image and in what context it appeared. Who published the image? What does the accompanying text (if any) say? Has the image been published by other people or media outlets? How does the image or accompanying text affect your feelings? If it seems designed to make you angry or seduce you, think about why.
How some organizations are combating the problem of dipfakes and AI-created misinformation
.
As we’ve seen, the methods that can help people distinguish between AI-generated images and real ones are still imperfect and limited. What’s worse, the spread of illegal or malicious AI images strikes a double blow, as such posts spread false information, which then breeds distrust in online media. But with the emergence of generative AI, several initiatives have also emerged to increase trust and transparency.
A few initiatives have been launched to increase trust and transparency.
The Coalition for Content Authentication (C2PA) was founded by Adobe and Microsoft and includes technology companies such as OpenAI and Google, as well as media companies such as Reuters and the BBC. C2PA provides clickable “content credentials” to determine the origin of images and whether they were created by AI. However, it is the responsibility of the image creators to attach these credentials.
And it is the responsibility of the creators of the images.
On the other hand, the Starling Lab at Stanford University is actively working on authenticating real images. Starling Lab verifies “sensitive digital records, such as documentation of human rights abuses, war crimes, and evidence of genocide,” and securely stores verified digital images on decentralized networks so that they cannot be tampered with. The lab’s work is not focused on end users, but its projects are a good resource for those who want to verify the authenticity of images, such as the war in Ukraine or the transfer of power from Donald Trump to Joe Biden.
Experts often talk about AI images in the context of deception and misinformation, but AI images aren’t always meant to deceive. Sometimes they’re just jokes or memes taken out of context, or they’re sloppy advertising. Or maybe it’s just a form of creative expression using an intriguing new technology. But whatever the case, AI images have become an integral part of our lives. And now you need to learn how to recognize them.