Intel Arrow Lake: everything we know about the 15th generation chips

Intel Arrow Lake, or Core Ultra 200, — is the next generation of Team Blue processors. Successors to the refreshed 14th-generation Meteor Lake/Raptor Lake, Arrow Lake is expected to debut in late 2024, but things aren’t as clear-cut as previous generations. It could appear alongside another low-power version to maximize Intel’s production capacity and do away with one of the longest-standing features of Intel processors: Hyperthreading.
Another low-power version of Arrow Lake is expected to be released in 2024.
There’s still some time before launch, so we don’t know all the details yet, and we’re not sure if these processors will turn out to be among the best in Intel’s lineup. Here’s everything you need to know about Intel Arrow Lake.
Here’s everything you need to know about Intel Arrow Lake.
Arrow Lake specs
Like Intel’s latest generations of processors, Arrow Lake will utilize a tiled design, with performance and efficiency cores working alongside the integrated GPU and other gas pedals for AI and video transcoding.
We don’t have specs broken down by model number yet, but Videocardz has compiled some alleged leaks from July that show a breakdown of the various Arrow Lake processor series.
The Core Ultra 9 models, the 285K and 275 (and possibly one more), will have eight performance cores, 16 efficient cores, and four Xe graphics cores. Their clock speeds will vary, but they should all have the same configuration of 24 processor cores. However, the clock speed may be lower than the last generation: rumor has it that it will be reduced by a few hundred MHz. Potentially, the top chip will have a maximum clock speed of 5.7 GHz. However, the frequency of the E core may increase to compensate for this.
It’s unclear if this is purely a design decision, or if it’s some sort of reaction to the recent controversy surrounding the 13900K and 14900K’s instability at higher clock speeds. However, it’s worth remembering that clock speed — is only one component of a chip’s performance. AMD processors have had lower clock speeds than Intel processors for many years, and yet they’ve withstood fierce competition just about everywhere else.
And yet AMD’s processors have been able to keep up with the competition.
The Core Ultra 7 models will have eight performance cores and 12 efficient cores, four more than the previous generation. They will come with and without four Xe graphics cores.
The Core Ultra 5 models will have the most configuration options, though they should all have six performance cores and eight efficient cores. There will be variants with and without graphics, more expensive variants with higher clock speeds, and some with a reduced number of GPU cores.
The Core Ultra 5 models will have the most configuration options, though all should come with six performance and eight efficient cores.
The new chips will have new core architectures. Arrow Lake P cores will reportedly be based on the Lion Cove architecture, while the efficiency cores will use the Skymont architecture. There are reports of a new core layout in which the E cores will be grouped between performance cores.
The new cores will be based on the Lion Cove architecture.
Arrow Lake will be built on the new LGA 1851 socket with more pins than the 12th and 13th generations on the LGA 1700 socket. This means that Arrow Lake processors will require a new motherboard, and you won’t be able to directly upgrade from a 12th-, 13th-, or 14th-generation PC. However, the physical socket size will be the same as the LGA 1700 socket, so the coolers should be compatible.
A Arrow Lake processors will need to be compatible.
The new socket will also bring with it a new generation of motherboard chipsets, as well as the mandatory use of DDR5 — no more DDR4 on this generation of Intel boards. Memory speed support will increase again, and there have been rumors of Thunderbolt 5 support, although these have not been confirmed. The flagship PCIe technology will also remain PCIe 5.
And the flagship PCIe technology will remain PCIe 5.
One major change that may come to Arrow Lake is that Intel will drop its long-standing simultaneous multi-threading technology — Hyperthreading. It did this in the lower-end models in the 9th generation, but the feature will reportedly be removed completely from top to bottom this year. The idea is to let the performance cores stretch out for demanding tasks, and the multi-threading that Hyperthreading normally provides will be handled by the new E and LP-E cores.
The idea is to let the performance cores stretch out for demanding tasks, and the multi-threading that Hyperthreading normally provides will be handled by the new E and LP-E cores.
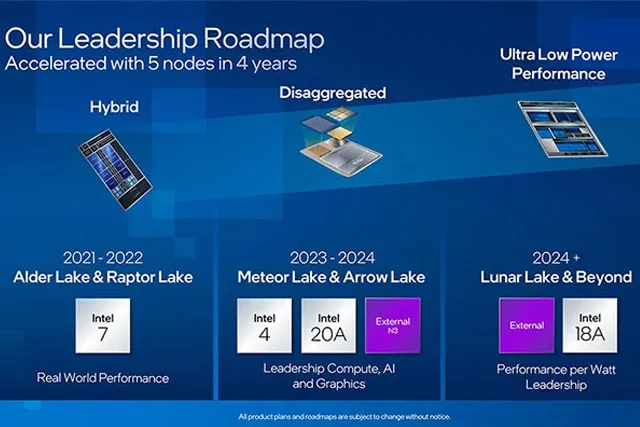
The Arrow Lake will reportedly be built using Intel’s 20A process node, which is commonly referred to as 2nm. The increased efficiency of this node may be the reason Intel has raised the temperature ceiling for Arrow Lake processors, giving them a maximum junction temperature of 105 degrees — 5 degrees higher than previous generations.
And it’s not just a matter of time before the processors will be built on the 20A node.
Bartlett Lake
It’s also rumored that Intel will introduce a new Bartlett Lake design for low-end processors alongside Arrow Lake in 2024, using the older 3nm Intel 4 design. These are probably intended to compete with AMD’s outdated but certainly unpopular Ryzen 5000 generation, which continues to get support in the form of new models like the 5700X3D and the new 5000 GT series.
They’re also rumored to be coming in the form of newer models like the 5700X3D and the new 5000 GT series.
The Barlett Lake will reportedly be based on the updated Raptor Lake silicon design, so it should be compatible with existing LGA 1700 platforms. It should also feature DDR4 memory, potentially making it a cheaper way to upgrade for Intel fans.
Additionally, it will be based on the Raptor Lake silicon design, so it should be compatible with existing LGA 17GA 17GA platforms.
While it may seem odd that Intel is using an older technology node and splitting its next-gen lineup into two parts, it’s to take pressure off the production of 20A silicon, which will be cutting-edge and in limited supply at the time of release. Using an older design for more affordable chips should improve availability and pricing by launch.
Silicon 20A should be available at the time of launch.
As of the latest rumors for July 2024, Bartlett Lake will come in several unique configurations, including a performance-only design with 12 P cores, as well as a more typical P + E design with Intel’s regular configurations.
Although these processors are unlikely to match the performance of Arrow Lake, the LGA 1700 socket expansion will be a great solution for those running on Intel’s existing platform.
Bartlett Lake is rumored to be released in January 2025.
Availability of Arrow Lake
When will Arrow Lake be available? The debut of the 14th-generation Meteor Lake was received mixedly by the company, so in order to stay on track with its plan to release five nodes in four years, Intel plans to launch Arrow Lake in the last months of 2024 — most likely alongside or shortly after Barlett Lake, in early 2025.
At the same time, Arrow Lake is expected to launch in the last months of 2024 — most likely alongside or shortly after Barlett Lake in early 2025.
According to the latest rumors, which surfaced in July, Arrow Lake’s launch would take place much closer to the end of the year, perhaps even in December. That should come after the sample validation phase is completed in September.
And it’s not expected to happen until the end of the year.
Lunar Lake is already rumored to be being tested by laptop manufacturers, so we could see mobile Lunar Lake processors soon after Arrow Lake debuts in desktop systems.
Lunar Lake is already being tested by laptop manufacturers, so we could see mobile Lunar Lake processors shortly after Arrow Lake debuts in desktop systems.
Arrow Lake performance
We don’t know how fast Arrow Lake will be yet, but thanks to a new core architecture, a new process node, and a higher temperature ceiling, they should be very fast. The clock speed rumors don’t mean too much at these speeds, but overclocking should help regain the speed advantage.
We don’t know how fast the Arrow Lake will be.
The announced IPC gains are about 5% for single-threaded and 15% for multi-threaded processors. The new process node and other improvements could lead to a noticeable performance boost in Arrow Lake.
The new process node and other improvements could lead to a noticeable performance increase in Arrow Lake.
And Arrow Lake will also add support for faster memory up to DDR5-6400, which should further boost performance.
And Arrow Lake will also add support for faster memory up to DDR5-6400, which should further boost performance.
The Arrow Lake integrated graphics are said to use Xe-LPG Plus, an updated version of the architecture we’ve seen in recent Arc and Meteor Lake GPUs. So it should be one of the fastest integrated graphics systems out there.
So it should be one of the fastest integrated graphics systems out there.






![Outcomes 2025: the memory crisis, agent-based AI and the failure of ultra-thin smartphones + [bonus] ForGeeks Podcast Outcomes 2025: the memory crisis, agent-based AI and the failure of ultra-thin smartphones + [bonus] ForGeeks Podcast](https://forgeeks.pro/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/exkwmm9t33zyr1hfbeeq.avif)
